Tempered glass has become one of the indispensable materials in many fields such as modern architecture, automobiles, home appliances, and electronic products. It not only has the light transmittance and aesthetics of traditional glass, but also is known as the "invisible shield" for its excellent mechanical strength and safety performance. It is this unique advantage that makes tempered glass show strong practical value and technical charm in various complex environments.
What is tempered glass? The strengthening process determines the performance
Tempered glass is a kind of safety glass formed by high-temperature treatment and rapid cooling on the basis of ordinary glass. Its core lies in the heat treatment process. By heating the glass to a point close to the softening point and then cooling it quickly, a strong compressive stress layer is formed on the surface of the glass. This compressive stress can significantly improve the impact resistance and bending resistance of the glass, making it stronger and more durable than ordinary glass.
The biggest technical challenge of the tempering process is the matching of temperature control accuracy and cooling speed. If handled improperly, the glass is prone to problems such as uneven stress and corner damage, which will affect the safety and stability of later use. Therefore, the top tempered glass manufacturers in the industry will pay special attention to the technical upgrades of furnace temperature distribution, airflow control and cooling systems to ensure that the overall performance of the glass is uniform and reliable.

In addition to high strength, safety performance is the key
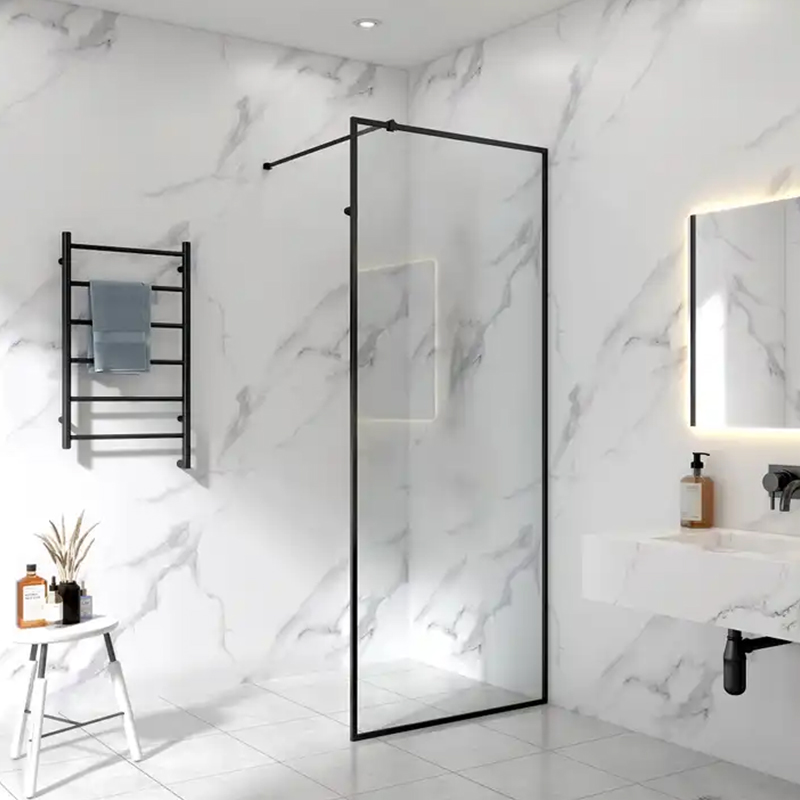
One of the most well-known characteristics of tempered glass is that it will not produce sharp fragments when it is damaged by external forces, but will break into small particles without edges, thereby greatly reducing the risk of injury to the human body. This "safe shattering" behavior is the core reason why it is widely used in public buildings, transportation facilities and consumer electronics.
Structurally, the surface compressive stress layer of tempered glass can effectively resist the invasion of external stress. When the glass is broken, the internal tensile stress is released instantly, and the whole piece of glass quickly breaks into small particles with blunt angles, thus avoiding the formation of long strips or sharp fragments when traditional glass is broken. This rupture method not only improves the safety level of the use scenario, but also lays a solid foundation for glass in industries with extremely high safety regulations.
Technical adaptability behind multi-scenario applications
With the increasing diversification of glass application scenarios, tempered glass is no longer an exclusive material in the construction field. From subway platform screen doors to smartphone screens, to furniture countertops and home appliance panels, tempered glass has penetrated into almost all product structures that are in close contact with people.
This high adaptability is inseparable from the continuous progress of glass thickness control, dimensional stability and edge processing technology. Especially in consumer electronics, tempered glass must be able to resist drops, scratches and even bending impacts while maintaining extreme transparency and touch sensitivity, which places extremely high demands on manufacturers' material selection, process execution and testing procedures.

Energy saving and environmental protection: the hidden advantages of tempered glass
As the concepts of green building and sustainable development are deeply rooted in people's hearts, the energy-saving and environmental protection characteristics of tempered glass have also begun to receive more attention. Its excellent thermal stability and high heat reflection ability make it an important material for improving energy efficiency in building facades and glass curtain wall applications.
Although tempered glass looks the same as ordinary glass, it shows "invisible power" in its subtle structure and deep performance. It not only protects every screen and every window in modern people's lives, but also silently demonstrates the high integration of scientific and technological manufacturing and material engineering. In the future material application landscape, tempered glass will remain a solid and dazzling cornerstone, leading multiple industries into a new era of higher quality and higher safety.



 中文简体
中文简体